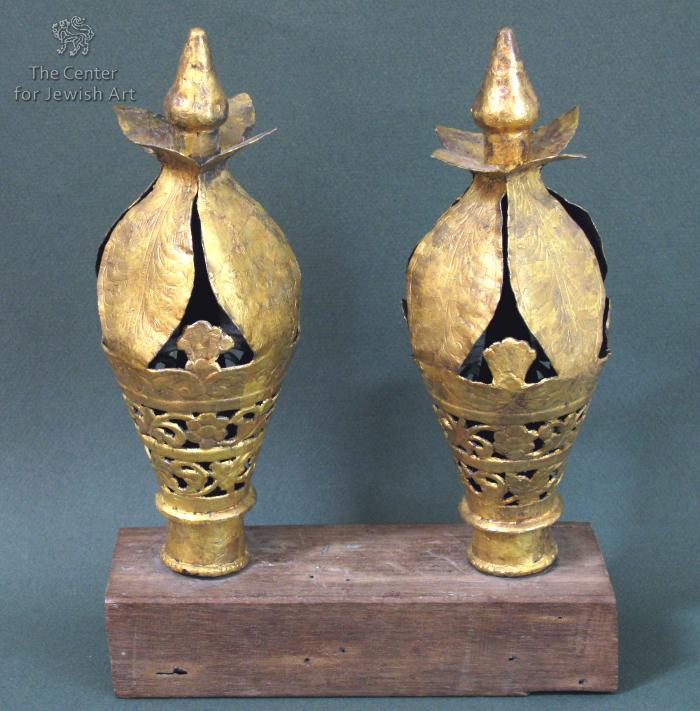
Obj. ID: 37165 Torah finials, Kochi (Cochin), circa 1850

sub-set tree:
The following description was prepared by William Gross:
The finials evolved from knobs at the upper end of the staves (Atzei Chaim) on which the Torah scroll is wound. Since the shape of the spherical finial recalled that of a fruit, it was called a tappu'aḥ, "apple," among the Jews of Spain and in the Sephardi Diaspora, and a rimmon, "pomegranate," in all other communities.
The earliest known reference to Torah finials occurs in a document from 1159, found in the Cairo Genizah, from which we learn that by the 12th century finials were already being made of silver and had bells. Around the same time, Maimonides mentions finials in the Mishneh Torah (Hilkhot Sefer Torah 10:4). Despite the variations on the spherical shape which developed over the centuries and the addition of small bells around the main body of the finial, the spherical, fruit-like form was the basic model for the design of finials in Oriental and European communities.
A most significant variation appeared in 15th-century Spain, Italy, and Germany, where the shape of finials was influenced by that of various objects of church ritual, whose design often incorporated architectural motifs, The resulting tower-like structure, which seems to have appeared around the same time in different parts of Europe, became the main type of finial in 18th-century Germany and Italy, as well as Morocco, brought there by Jews expelled from Spain.
This rather small pair of Torah finials, or "Rimmonim" in Hebrew, was used on the Torah Tik favored by the Jews of Cochin. Shaped in the form of a lotus flower, the pair is crafted from silver covered with gold leaf. There is a similar pair in the Jewish museum in New York. This form is unique to the Jews of the Cochin area. The Torah Tiks and the crowns used in that city were also unusual forms linked to that area only.
The Jewish community of Cochin boasts a history of almost one thousand years, but only a handful of Jews remain there today. After the establishment of the State of Israel, almost all of the Jews immigrated to that country.